Photo from wikipedia
Alzheimer's disorder is one of the most common world-wide health problems and its prevalence continues to increase thereby straining the healthcare budgets of both developed and developing countries. We report… Click to show full abstract
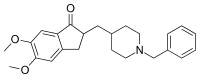
Alzheimer's disorder is one of the most common world-wide health problems and its prevalence continues to increase thereby straining the healthcare budgets of both developed and developing countries. We report herein a new donepezil-like natural compound derivative (D1) as a convincing AChE inhibitor. The in silico studies suggests that D1 exhibits a dual-binding mode of action and interacts with both the catalytic anionic site and PAS of human AChE. The biological studies confirm the dual binding site character of D1 and revealed that D1 not only enhances the acetylcholine levels but also reduces the accumulation of Aβ plaques in C. elegans. In fact, 5μM of D1 was seen more potent in elevating the acetylcholine expression than 15μM of donepezil. While most of the noncholinergic functions of donepezil associated with the PAS of AChE were gradually lost at higher concentrations, D1 was more functional at similar doses. Promisingly, D1 also exerted agonistic effect on the α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor.
Journal Title: Journal of chemical information and modeling
Year Published: 2020
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!