Photo from wikipedia
Fusion pores serve as an effective mechanism to connect intracellular organelles and release vesicle contents during exocytosis. A complex lipid rearrangement takes place as membranes approximate, bend, fuse, and establish… Click to show full abstract
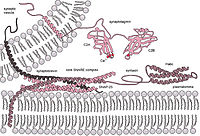
Fusion pores serve as an effective mechanism to connect intracellular organelles and release vesicle contents during exocytosis. A complex lipid rearrangement takes place as membranes approximate, bend, fuse, and establish a traversing water channel to define the fusion pore, linking initially isolated chambers. Thermodynamically, the process is unfavorable and thought to be mediated by specialized proteins. In this work, we have developed a reaction coordinate to induce fusion pores from initially flat and parallel lipid bilayers and we have used it to describe the effects of the synaptotagmin-1 C2B domain during the process. We have obtained free-energy profiles of the whole lipid reorganization in biologically realistic membranes, going from planar and parallel bilayers through stalk hemifusion to water channel formation. Our results point to a lysine-rich polybasic region on synaptotagmin-1 C2B as the key to lipid reorganization control through the formation of phosphatidylinositol bisphosphate clusters that stabilize the fusion pore.
Journal Title: Journal of chemical theory and computation
Year Published: 2020
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!