Photo from wikipedia
Ketonization of carboxylic acids on metal oxides enables oxygen removal and the formation of new C–C bonds for increasing the energy density and chemical value of biomass-derived streams. Information about… Click to show full abstract
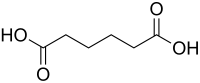
Ketonization of carboxylic acids on metal oxides enables oxygen removal and the formation of new C–C bonds for increasing the energy density and chemical value of biomass-derived streams. Information about the surface coverages and reactivity of various bound species derived from acid reactants and the kinetic relevance of the elementary steps that activate reactants, form C–C bonds, and remove O atoms and how they depend on acid–base properties of surfaces and molecular properties of reactants is required to extend the range of ketonization catalytic practice. Here, we examine such matters for ketonization of C2–C4 carboxylic acids on monoclinic and tetragonal ZrO2 (ZrO2(m), ZrO2(t)) materials that are among the most active and widely used ketonization catalysts by combining kinetic, isotopic, spectroscopic, and theoretical methods. Ketonization turnovers require Zr–O acid–base pairs, and rates, normalized by the number of active sites determined by titration methods during catalysis, are slightly higher...
Journal Title: Journal of Physical Chemistry C
Year Published: 2017
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!