Photo from wikipedia
Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) remains a deadly infectious disease despite existing antiretroviral therapies. A comprehensive understanding of the specific mechanisms of viral infectivity remains elusive and currently limits… Click to show full abstract
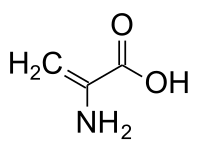
Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) remains a deadly infectious disease despite existing antiretroviral therapies. A comprehensive understanding of the specific mechanisms of viral infectivity remains elusive and currently limits the development of new and effective therapies. Through in-depth proteomic analysis of HIV-1 virions, we discovered the novel post-translational modification of highly conserved residues within the viral matrix and capsid proteins to the dehydroamino acids, dehydroalanine and dehydrobutyrine. We further confirmed their presence by labeling the reactive alkene, characteristic of dehydroamino acids, with glutathione via Michael addition. Dehydroamino acids are rare, understudied, and have been observed mainly in select bacterial and fungal species. Until now, they have not been observed in HIV proteins. We hypothesize that these residues are important in viral particle maturation and could provide valuable insight into HIV infectivity mechanisms.
Journal Title: Journal of proteome research
Year Published: 2022
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!