Photo from wikipedia
Environmentally friendly blue-emitting ZnSe quantum dots (QDs) are in high demand for next-generation light-emitting devices. Yet, they suffer longstanding optical instability issues under aerobic conditions. Herein, we have demonstrated the… Click to show full abstract
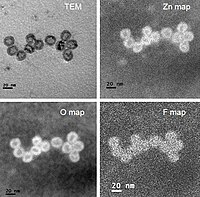
Environmentally friendly blue-emitting ZnSe quantum dots (QDs) are in high demand for next-generation light-emitting devices. Yet, they suffer longstanding optical instability issues under aerobic conditions. Herein, we have demonstrated the existence of oxidization or hydroxylation on the QD surface when QDs are subjected to oxygen exposure, which potentially introduces highly localized in-gap states. Those states result in a dense number of surface-related, weak-intensity "dark" exciton states at the emission edge. Remarkably, there exists a critical diameter (Dc ≈ 8.5 nm) at which the deepest trap level reaches resonance with the highest occupied molecular orbital state. Beyond this critical diameter, the effects of those trap states are minimized, and the emission edge is dominated by high-intensity, bulk-to-bulk-like "bright" exciton states. The present work provides a novel strategy for designing highly stable QD emitters via size engineering, which are broadly applicable to other closely related QD systems.
Journal Title: Nano letters
Year Published: 2022
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!