Photo from wikipedia
The use of biocompatible materials and fabrication methods is of particular importance in the development of wound dressings. Cellulose acetate (CA) has excellent properties for wound dressing applications, but it… Click to show full abstract
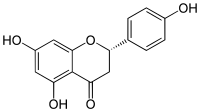
The use of biocompatible materials and fabrication methods is of particular importance in the development of wound dressings. Cellulose acetate (CA) has excellent properties for wound dressing applications, but it is insufficient for the wound healing process due to its lack of bioactive and antibacterial properties. In this study, CA was electrospun with retinyl palmitate (RP) and clove essential oil (CLV) to fabricate a novel antibacterial and antioxidant biomaterial. The effects of RP and CLV incorporation on the surface morphology, fiber diameter, antioxidant activity, antibacterial activity, cell viability, and release behavior of the fabricated CA mats were investigated. In light of these studies, it was determined that the nanofiber mat, fabricated with a 15% w/v CA polymer concentration, a 1% w/w RP ratio, and a 5% w/w CLV ratio, was biocompatible with L929 fibroblast cells with antibacterial and antioxidant properties. Overall, results showed that this nanofiber offers promise for use as a wound dressing.
Journal Title: ACS Omega
Year Published: 2023
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!