Photo from wikipedia
As efforts are made toward establishing a circular economy that engages in activities that maintain resources at their highest values for as long as possible, an important aspect is understanding… Click to show full abstract
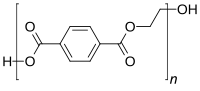
As efforts are made toward establishing a circular economy that engages in activities that maintain resources at their highest values for as long as possible, an important aspect is understanding the systems which allow recycling to occur. In this article a common plastic, polyethylene terephthalate, i.e., PET or plastic #1, has been studied because it is recycled at relatively high rates in the U.S. as compared to other plastics. A material flow analysis is described for PET resin showing materials collected, reclaimed for flake, and converted into items with recycled content. Imports/exports, reclaimer residue, and disposal with mismanaged waste are all shown for U.S. flows of PET. Barriers to recycling PET exist in the collecting, sorting, reclaiming, and converting steps, and this article describes them, offers some solutions, and suggests some research that chemists and engineers could focus on to improve the systems. This effort also models sorting at material recovery facilities (MRF) and reclaimers, with detailed descriptions of the material streams involved, to characterize the resource use and emissions from these operations that are key processes in the recycling system. Example results include greenhouse gas intensities of 8.58 kg CO2 equiv per ton of MRF feed and 103.7 kg CO2 equiv per ton of reclaimer PET bale feed. The results can be used in system analyses for various scenarios and as inputs in economic input-output and life cycle assessments.
Journal Title: ACS sustainable chemistry & engineering
Year Published: 2022
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!