Photo from wikipedia
We have developed a new, aqueous-based process for production of superabsorbent materials that is catalyst-free and eco-friendly as the superabsorbent was derived from two completely biodegradable polymers with water as… Click to show full abstract
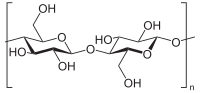
We have developed a new, aqueous-based process for production of superabsorbent materials that is catalyst-free and eco-friendly as the superabsorbent was derived from two completely biodegradable polymers with water as the only byproduct. The new hydrogels were obtained by cross-linking partially oxidized bleached kraft pulp fibers with carboxymethylated chitosan. In distilled water, the maximum water retention value (WRV) of the cross-linked hydrogels reached 610 (g/g gel), which is several times higher than any neat cellulose-based superabsorbent material reported in the literature. In saline water, the WRV of the new hydrogels (85 g/g) doubled that of commercial gels (40–50 g/g). In the presence of potassium or ammonium cations, the WRV increased further to reach 91 and 96 g/g, respectively. Gels only lost 5–10% of their reswelling capacity when reused four consecutive times. The hydrogels had high porous architecture and specific surface area that facilitates rapid mass penetration in superabsorbent ...
Journal Title: ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering
Year Published: 2018
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!