Photo from wikipedia
To evaluate the association between hypocapnia within the first 24 h of life and brain injury assessed by a detailed MRI scoring system in infants receiving therapeutic hypothermia (TH) for neonatal… Click to show full abstract
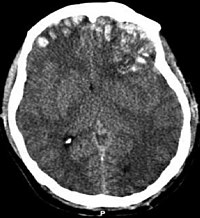
To evaluate the association between hypocapnia within the first 24 h of life and brain injury assessed by a detailed MRI scoring system in infants receiving therapeutic hypothermia (TH) for neonatal encephalopathy (NE) stratified by the stage of NE. This retrospective cohort study included infants who received TH for mild to severe NE. 188 infants were included in the study with 48% having mild and 52% moderate-severe NE. Infants with moderate-severe NE spent more time in hypocapnia (PCO2 ≤ 35 mmHg) and presented with more severe brain injury on MRI compared to mild cases. The MRI injury score increased by 6% for each extra hour spent in hypocapnic range in infants with moderate-severe NE. There was no association between hypocapnia and injury scores in mild cases. In infants with moderate-severe NE, the hours spent in hypocapnia was an independent predictor of brain injury.
Journal Title: Journal of Perinatology
Year Published: 2022
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!