Photo from wikipedia
Synaptic dysfunction is hypothesised to play a key role in schizophrenia pathogenesis, but this has not been tested directly in vivo. Here, we investigated synaptic vesicle glycoprotein 2A (SV2A) levels… Click to show full abstract
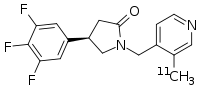
Synaptic dysfunction is hypothesised to play a key role in schizophrenia pathogenesis, but this has not been tested directly in vivo. Here, we investigated synaptic vesicle glycoprotein 2A (SV2A) levels and their relationship to symptoms and structural brain measures using [ 11 C]UCB-J positron emission tomography in 18 patients with schizophrenia and 18 controls. We found significant group and group-by-region interaction effects on volume of distribution ( V T ). [ 11 C]UCB-J V T was significantly lower in the frontal and anterior cingulate cortices in schizophrenia with large effect sizes (Cohen’s d = 0.8-0.9), but there was no significant difference in the hippocampus. We also investigated the effects of antipsychotic drug administration on SV2A levels in Sprague-Dawley rats using western blotting, [ 3 H]UCB-J autoradiography and immunostaining with confocal microscopy, finding no significant effects on any measure. These findings indicate that there are lower synaptic terminal protein levels in schizophrenia in vivo and that antipsychotic drug exposure is unlikely to account for them. Synaptic dysfunction is hypothesised to play a key role in schizophrenia pathogenesis. Here, using [ 11 C]UCB-J PET, the authors show for the first time in vivo that levels of the synaptic marker protein SV2A are reduced in schizophrenia and unaffected by antipsychotic treatment in a rat model.
Journal Title: Nature Communications
Year Published: 2020
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!