Photo from wikipedia
Cytosolic phospholipase A2 (cPLA2) is an enzyme that releases arachidonic acid (AA) for the synthesis of eicosanoids and lysophospholipids which play critical roles in the initiation and modulation of oxidative… Click to show full abstract
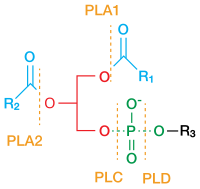
Cytosolic phospholipase A2 (cPLA2) is an enzyme that releases arachidonic acid (AA) for the synthesis of eicosanoids and lysophospholipids which play critical roles in the initiation and modulation of oxidative stress and neuroinflammation. In the central nervous system, cPLA2 activation is implicated in the pathogenesis of various neurodegenerative diseases that involves neuroinflammation, thus making it an important pharmacological target. In this paper, a new class of arachidonic acid (AA) analogues was synthesized and evaluated for their ability to inhibit cPLA2. Several compounds were found to inhibit cPLA2 more strongly than arachidonyl trifluoromethyl ketone (AACOCF3), an inhibitor that is commonly used in the study of cPLA2-related neurodegenerative diseases. Subsequent experiments concluded that one of the inhibitors was found to be cPLA2-selective, non-cytotoxic, cell and brain penetrant and capable of reducing reactive oxygen species (ROS) and nitric oxide (NO) production in stimulated microglial cells. Computational studies were employed to understand how the compound interacts with cPLA2.
Journal Title: Scientific Reports
Year Published: 2017
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!