Photo from wikipedia
Bats are natural reservoirs for potential zoonotic viruses. In this study, next-generation sequencing was performed to obtain entire genome sequences of picornavirus from a picornavirus-positive bat feces sample (16BF77) and… Click to show full abstract
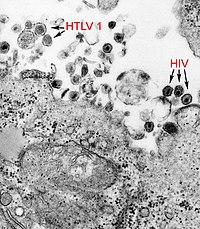
Bats are natural reservoirs for potential zoonotic viruses. In this study, next-generation sequencing was performed to obtain entire genome sequences of picornavirus from a picornavirus-positive bat feces sample (16BF77) and to explore novel viruses in a pooled bat sample (16BP) from samples collected in South Korea, 2016. Fourteen mammalian viral sequences were identified from 16BF77 and 29 from 16BP, and verified by RT-PCR. The most abundant virus in 16BF77 was picornavirus. Highly variable picornavirus sequences encoding 3Dpol were classified into genera Kobuvirus, Shanbavirus, and an unassigned group within the family Picornaviridae. Amino acid differences between these partial 3Dpol sequences were ≥ 65.7%. Results showed that one bat was co-infected by picornaviruses of more than two genera. Retrovirus, coronavirus, and rotavirus A sequences also were found in the BP sample. The retrovirus and coronavirus genomes were identified in nine and eight bats, respectively. Korean bat retroviruses and coronavirus demonstrated strong genetic relationships with a Chinese bat retrovirus (RfRV) and coronavirus (HKU5-1), respectively. A co-infection was identified in one bat with a retrovirus and a coronavirus. Our results indicate that Korean bats were multiply infected by several mammal viruses.
Journal Title: Scientific Reports
Year Published: 2020
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!