Photo from wikipedia
A general strategy has been developed here to co-assemble polyoxometalates (POMs) and polymers into core–shell hybrid nanoparticles via hydrogen bonding interaction. Due to the hydrogen bonds between the pyridine groups… Click to show full abstract
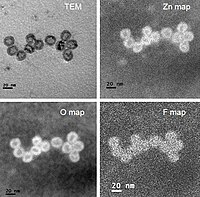
A general strategy has been developed here to co-assemble polyoxometalates (POMs) and polymers into core–shell hybrid nanoparticles via hydrogen bonding interaction. Due to the hydrogen bonds between the pyridine groups of poly(4-vinyl pyridine) (P4VP) and the hydrogen bonding donor groups on the POM surface, P4VP is stabilized by the POMs and dispersed as discrete hybrid core–shell nanoparticles in aqueous solution. For these thermodynamically stable nanoparticles, the P4VP cores are covered with hexagonal close-packed POMs. The size of the core–shell particles is controlled by the electrostatic repulsive interaction among the POMs. The introduction of extra salts screens the repulsive force among the POMs, thus increasing the size of the core–shell structures.
Journal Title: Materials Chemistry Frontiers
Year Published: 2018
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!