Photo from wikipedia
OBJECTIVES Peristomal leakage, infection, and persisting fistula after tube removal are rare, but well-known complications in long-term percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomies (PEG). A standard treatment procedure is missing. This case series… Click to show full abstract
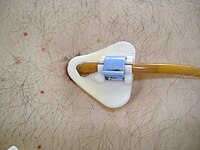
OBJECTIVES Peristomal leakage, infection, and persisting fistula after tube removal are rare, but well-known complications in long-term percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomies (PEG). A standard treatment procedure is missing. This case series describes a procedure of tube removal, tailored antibiotic therapy and endoscopic closure with a gastropexy device after mechanical de-epithelialization of the fistulous tract. CASE PRESENTATION Three patients with infected long-standing PEG (4 to 21 years) were included. The tubes were removed endoscopically and tailored antimicrobial therapy was administered over 10 to 14 days. The persisting fistula was de-epithelialized mechanically and sutured under endoscopic control with a dedicated gastropexy device 11 to 25 days thereafter. A new PEG tube was placed in the same session on a different site. After 30 days the fistula had healed completely, and the PEG worked well in all subjects. CONCLUSIONS Endoscopic sealing of a persisting fistula with a dedicated gastropexy device after thorough de-epithelialization is a promising technique that needs confirmation by larger studies.
Journal Title: Zeitschrift fur Gastroenterologie
Year Published: 2022
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!