Photo from wikipedia
A superhydrophobic surface is non-sticking to aqueous droplets due to minimized solid-liquid contact, but the small contact area also poses challenges to droplet maneuvering. This letter reports a technique using… Click to show full abstract
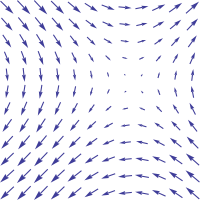
A superhydrophobic surface is non-sticking to aqueous droplets due to minimized solid-liquid contact, but the small contact area also poses challenges to droplet maneuvering. This letter reports a technique using electric field gradients to actuate aqueous droplets on superhydrophobic surfaces. A pin-ring electrode pair underneath the insulating superhydrophobic surface is used to generate electric field gradient above the surface, with the field focused around the pin. The non-uniform field operates on the electrostatically induced charges on the droplet, producing an actuation force attracting the droplet toward the pin. The actuation force is proportional to the square of the imposed field as shown in both experiments and simulations. This non-contact actuation technique is effective in electrostatically trapping and translating superhydrophobic droplets, despite the small solid-liquid contact. The pin-ring configuration can be readily extended to a pin array between two parallel lines, which essentially form a stretched ring closing at infinity. The pin array is used to demonstrate individual actuation of two droplets leading to their eventual coalescence.A superhydrophobic surface is non-sticking to aqueous droplets due to minimized solid-liquid contact, but the small contact area also poses challenges to droplet maneuvering. This letter reports a technique using electric field gradients to actuate aqueous droplets on superhydrophobic surfaces. A pin-ring electrode pair underneath the insulating superhydrophobic surface is used to generate electric field gradient above the surface, with the field focused around the pin. The non-uniform field operates on the electrostatically induced charges on the droplet, producing an actuation force attracting the droplet toward the pin. The actuation force is proportional to the square of the imposed field as shown in both experiments and simulations. This non-contact actuation technique is effective in electrostatically trapping and translating superhydrophobic droplets, despite the small solid-liquid contact. The pin-ring configuration can be readily extended to a pin array between two parallel lines, which essential...
Journal Title: Applied Physics Letters
Year Published: 2019
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!