Photo from wikipedia
Fluctuations refer to inhomogeneity in the distribution of donors and acceptors at the nanometer scale and occur in many compound solar cell materials such as Cu(In,Ga)Se2, Cu2ZnSn(S,Se)4, and CdSexTe1−x. In… Click to show full abstract
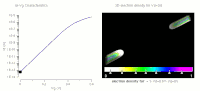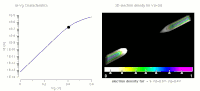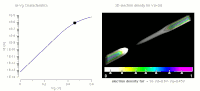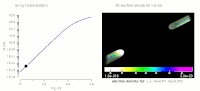
Fluctuations refer to inhomogeneity in the distribution of donors and acceptors at the nanometer scale and occur in many compound solar cell materials such as Cu(In,Ga)Se2, Cu2ZnSn(S,Se)4, and CdSexTe1−x. In this work, numerical simulations show that these fluctuations produce not only electrostatic potential variation, but also, local changes in the carrier density and effective bandgap. For a CdSexTe1−x absorber doped with arsenic, simulations and cathodoluminescence data within single grains demonstrate how donor and acceptor densities—consistent with capacitance-voltage and secondary-ion mass-spectrometry data—produce tails in photoluminescence, quantum efficiency, and absorption measurements. Using multiple theoretical approaches, we demonstrate that the fluctuations can hinder expected performance gains from increased carrier density, and we describe the significant open-circuit voltage deficit observed in the CdSexTe1−x:As solar technology. Our results demonstrate that it is critical to characterize and reduce carrier compensation to realize a higher efficiency.
Journal Title: Journal of Applied Physics
Year Published: 2020
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!