Photo from wikipedia
Significance Thymic stromal cells impose T cell self-tolerance by presenting self-antigens to developing T cells and inducing apoptosis in strongly self-reactive cells, a process known as clonal deletion. Self-antigen presentation… Click to show full abstract
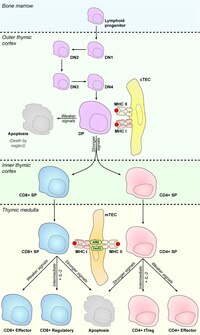
Significance Thymic stromal cells impose T cell self-tolerance by presenting self-antigens to developing T cells and inducing apoptosis in strongly self-reactive cells, a process known as clonal deletion. Self-antigen presentation is facilitated by particularly high levels of basal autophagy in thymic stromal cells, but the mechanisms regulating this constitutive autophagy have not been clear. Here, we find that high basal autophagy in thymic stromal cells depends on conspicuously low expression of the hydrogen peroxide–quenching enzyme catalase and that the highly oxidative redox status of thymic stromal cells promotes T cell clonal deletion and self-tolerance in an autophagy-dependent manner. These studies suggest that tightly regulated catalase expression promotes thymic stromal cell autophagy and central T cell tolerance.
Journal Title: Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America
Year Published: 2022
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!