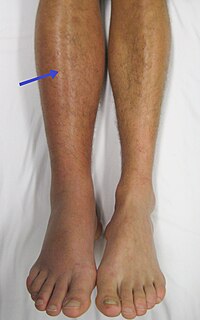
Photo from wikipedia
Abstract Background Extended antithrombotic treatment is recommended for secondary prevention of unprovoked venous thromboembolism (VTE), however, there is no consensus on which antithrombotic strategy is preferable. Aim To compare the… Click to show full abstract
Abstract Background Extended antithrombotic treatment is recommended for secondary prevention of unprovoked venous thromboembolism (VTE), however, there is no consensus on which antithrombotic strategy is preferable. Aim To compare the efficacy and safety of different antithrombotic strategies for secondary prevention unprovoked VTE. Methods Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials, Embase, and MEDLINE were systematically searched from inception to 22 July 2020 for randomized controlled trials (RCTs) that compared the efficacy and/or safety of extended antithrombotic strategies including aspirin, warfarin and direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs) for secondary prevention of unprovoked VTE. The primary outcome was risk of major bleeding and the secondary outcomes were risks of recurrent VTE and all-cause death. Odds ratios (ORs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were estimated using pairwise and network meta-analysis with random effect. Possible ranking of extended antithrombotic strategies was plotted using the surface under the cumulative ranking curve and mean ranks. Results Seventeen RCTs met the inclusion criteria, and meta-analysis results showed that warfarin was associated with significantly higher risk of major bleeding than placebo/observation (OR 2.71, 95% CI 1.32–5.55) or apixaban (OR 10.65, 95% CI 1.06–107.13). Apixaban and low-apixaban were the top two strategies according to the ranking of major bleeding. Warfarin (OR 0.25, 95%CI 0.13–0.49), rivaroxaban (OR 0.18, 95%CI 0.03–0.90), apixaban (OR 0.18, 95%CI 0.04–0.85) and low-apixaban (OR 0.18, 95%CI 0.04–0.82) were related to significantly lower risk than placebo/observation; edoxaban was non-inferior to warfarin on the risk of recurrent VTE. Furthermore, apixaban was linked with significantly lower risk of all-cause death than placebo/observation (OR 0.29, 95% CI 0.09–0.88). Conclusion Apixaban showed superiority to other antithrombotic strategies on major bleeding and all-cause death for secondary prevention of unprovoked VTE. Further studies are warranted owing to the limited number of studies and positive cases. Key messages All antithrombotic strategies including warfarin, DOACs and aspirin were superior to placebo/observation on recurrent VTE for secondary prevention of unprovoked VTE. Apixaban demonstrated lower risk of major bleeding than warfarin, and lower risk of all-cause death than placebo/observation. Further research about the efficacy and safety of antithrombotic treatments for secondary prevention of unprovoked VTE is warranted.
Journal Title: Annals of Medicine
Year Published: 2022
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!