Photo from wikipedia
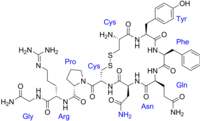
ABSTRACT Introduction: Thymosin beta-4 (Tβ4) is an actin sequestering protein and is furthermore involved in diverse biological processes including cell proliferation, differentiation, wound healing, stem- or progenitor cell differentiation, and… Click to show full abstract
ABSTRACT Introduction: Thymosin beta-4 (Tβ4) is an actin sequestering protein and is furthermore involved in diverse biological processes including cell proliferation, differentiation, wound healing, stem- or progenitor cell differentiation, and modulates inflammatory mediators. Tβ4 also attenuates fibrosis. However, the role of Tβ4 in cardiomyocytes hypertrophy is unknown. Areas covered: In this review, we will discuss the role of Tβ4 in cardiac remodeling that specifically includes cardiac hypertrophy and fibrosis only. Our review will further cover a new signaling pathway, the wingless and integrated-1 (Wnt) pathway in cardiac remodeling. In rat neonatal and adult cardiomyocytes stimulated with angiotensin II (Ang II), we showed that Tβ4 has the ability to reduce cell sizes, attenuate hypertrophy marker genes expression, along with a panel of WNT-associated gene expressions induced by Ang II. Selected target gene WNT1-inducible-signaling pathway protein 1 (WISP-1) was identified by Tβ4. Data further confirmed that WISP-1 overexpression promoted cardiomyocytes growth and was reversed by Tβ4 pretreatment. Expert opinion: Our data suggested that Tβ4 protects cardiomyocytes from hypertrophic response by targeting WISP-1. The new role of Tβ4 in cardiac hypertrophy advances our understanding, and the mechanism of action of Tβ4 may provide a solid foundation for the treatment of cardiac disease.
Journal Title: Expert Opinion on Biological Therapy
Year Published: 2018
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!