Photo from wikipedia
Abstract Background Infantile Hemangiopericytoma (HPC)/Solitary Fibrous Tumor (SFT), a vascular tumor of head and neck region, can be congenital or arise during the first year of the life. As the… Click to show full abstract
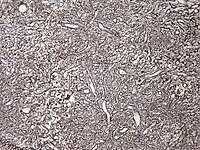
Abstract Background Infantile Hemangiopericytoma (HPC)/Solitary Fibrous Tumor (SFT), a vascular tumor of head and neck region, can be congenital or arise during the first year of the life. As the infantile form of hemangiopericytoma has a better course than the adult form, surgical excision is recommended. Case Report: A full-term neonate presented with a congenital right temporal soft tissue mass. MRI revealed a highly vascular mass with a hemorrhagic and possible necrotic core without intracranial extension. The lesion grew in 2 weeks from 4x4 cm to 9x7 cm. Histologically, a hypercellular spindle cell mesenchymal neoplasm had prominent staghorn vessels, alternating with hypocellular areas. Mitotic activity was low(1-3/HPF) and necrosis was absent. Conclusion: Infantile HPC/SFT of head and neck can grow rapidly during the infantile period. Complete excision without mutilating surgery should be curative.
Journal Title: Fetal and Pediatric Pathology
Year Published: 2020
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!