Photo from wikipedia
Abstract Background: Some studies have estimated the diagnostic value of procalcitonin (PCT) for Kawasaki disease (KD), but the results are not always consistent. The aim of this study was to… Click to show full abstract
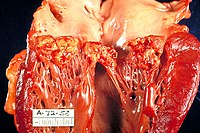
Abstract Background: Some studies have estimated the diagnostic value of procalcitonin (PCT) for Kawasaki disease (KD), but the results are not always consistent. The aim of this study was to ascertain the diagnostic value of PCT for KD. Methods: Relevant and eligible articles assessing the diagnostic significance of PCT in KD were systematically searched from PubMed as well as the CNKI databases (last update: October 31, 2020), followed by bivariate models to evaluate the overall diagnostic significance of PCT in KD. This systematic review and meta-analysis included four articles. Results: The overall diagnostic specificity and sensitivity were 0.78 (95% CI: 0.74–0.82) and 0.73 (95% CI: 0.69–0.76), respectively. The area under the summary receiver operating characteristic (sROC) curve (AUC) was 0.82. The negative likelihood ratio (NLR) and positive likelihood ratio (PLR) values for PCT were 0.34 and 3.23, respectively. Conclusions: By analyzing the accessible articles, we showed PCT is not a particularly useful test for KD diagnosis.
Journal Title: Fetal and Pediatric Pathology
Year Published: 2022
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!