Photo from wikipedia
ABSTRACT Aim To systematically review the effectiveness of physical therapy interventions in infants, children and adolescents with brachial plexus birth injury (BPBI). Methods Systematic review of randomized controlled trials including… Click to show full abstract
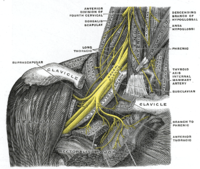
ABSTRACT Aim To systematically review the effectiveness of physical therapy interventions in infants, children and adolescents with brachial plexus birth injury (BPBI). Methods Systematic review of randomized controlled trials including patients under 18 years old with BPBI was conducted on Medline, Cochrane, Embase, Amed and Pedro databases. Methodological quality was assessed by the PEDro score and quality of evidence by the GRADE system. The primary outcomes measured were range of motion, muscle strength and bone mineral density. Results Seven studies were included, two in infant and 5 in children, of 932 title and abstracts screened. The interventions, characteristics of the participants and outcomes were diverse. The largest effect was found when other intervention was combined with conventional physical therapy in the primary outcomes, with low quality of evidence. Conclusion Physical therapy interventions alone or in combination with other treatment modalities are effective in improving short-term disabilities in children with BPBI.
Journal Title: Developmental Neurorehabilitation
Year Published: 2022
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!