Photo from wikipedia
ABSTRACT Poly(ε-L-lysine) and poly(L-diaminopropionic acid) are valuable homopoly (amino acids) with antimicrobial properties and mainly produced in submerged fermentation. In this study, we investigated their co-production using waste biomass and… Click to show full abstract
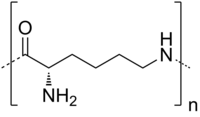
ABSTRACT Poly(ε-L-lysine) and poly(L-diaminopropionic acid) are valuable homopoly (amino acids) with antimicrobial properties and mainly produced in submerged fermentation. In this study, we investigated their co-production using waste biomass and spent mushroom substrate in solid-state fermentation. Simultaneous production of poly(L-diaminopropionic acid) and poly(ε-L-lysine) was achieved in a single fermentation process using pearl oyster mushroom residues as substrate, with the supplement of glycerol and corn steep liquor. After optimization of the fermentation parameters, the maximum yield of poly(ε-L-lysine) and poly(L-diaminopropionic acid) reached 51.4 mg/g substrate and 25.4 mg/g substrate, respectively. The optimal fermentation conditions were 70% initial moisture content, pH of 6.5, 30°C and an inoculum size of 14%. Furthermore, the fermentation time was reduced from 8 days to 6 days using repeated-batch solid-state fermentation. Finally, the antimicrobial effects of poly(L-diaminopropionic acid) and poly(ε-L-lysine) were evaluated in freshly pressed grape juice, which indicated tremendous potential of this mixture in its use as biological preservative. Graphical Abstract
Journal Title: Bioengineered
Year Published: 2022
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!