Photo from wikipedia
Abstract The exploration of relationship between orchid and its endophytic fungi is significant as vast arrays of beneficial attributes are provided by the fungi to its host which includes the… Click to show full abstract
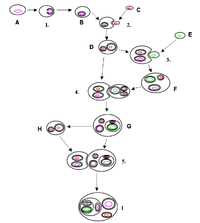
Abstract The exploration of relationship between orchid and its endophytic fungi is significant as vast arrays of beneficial attributes are provided by the fungi to its host which includes the production of phytohormones like Indole acetic acid (IAA). The present investigation focused on production, characterization and applications of IAA from endophytic fungi of Cymbidium aloifolium, an epiphytic orchid. The Colletotrichum gloeosporioides (CAR4) isolated and characterized from C. aloifolium produced higher Indole acetic acid (10.7±1.97 ìM/mL). The CAR4 IAA produced was confirmed by UV/Vis spectrum, TLC, FTIR, HPLC, LCMS, NMR analysis. The CAR4 IAA treated Macrotyloma uniflorum and Vigna unguiculata seeds exhibited increased germination percentage by 3 - 8 %, root length by 1 - 14 mm, shoot length by 2 - 21 mm compared to standard IAA. The Murashige and Skoog’s Basal media (MSBM) with coconut milk (10 %), casein hydrolysate (250 mg/L) showed swelling of C. aloifolium seeds within 15 days and well developed protocorms after 60 days of incubation. The differentiation of protocorms into roots and shoots was higher in MSBM with CAR4 IAA (0.5 mg/L) and BAP (6-Benzylaminopurine) (1 mg/L) with average of 8.5 ± 0.83 shoots and 5.67 ± 0.81 roots. The culture parameters were optimized and maximum IAA production was in PDB with 4 mg/mL of ⟨-tryptophan, pH6, 30°C, 15 days incubation in dark. IAA production increased four folds with optimized parameters.
Journal Title: Journal of Biologically Active Products from Nature
Year Published: 2019
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!