Photo from wikipedia
Core–shell structures with ZnO cores have been widely investigated due to their effectiveness in suppressing surface defects of ZnO nanostructures. As the surface defects are hugely dependent on the synthesis… Click to show full abstract
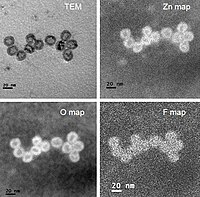
Core–shell structures with ZnO cores have been widely investigated due to their effectiveness in suppressing surface defects of ZnO nanostructures. As the surface defects are hugely dependent on the synthesis conditions, it is important to understand the interactions between shell material and ZnO with different surface chemistry. Here we produce well-aligned ZnO nanorods using two growth methods, leading to ZnO with different surface chemistries. A thin layer of TiO2 shell is applied via layer-by-layer adsorption method. The core–shell structure is confirmed via high-resolution transmission electron microscopy. The optical properties and chemical states of both bare nanorods and core–shell structures are investigated and compared using photoluminescence (PL) measurement and x-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). Both PL and XPS results suggest surface defects are passivated by TiO2 shell coating. The shell coating has a stronger effect on ZnO synthesized in OH− rich environment, due to excessive hydroxyl groups provided during synthesis, which remain even after annealing-induced crystallization.
Journal Title: Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics
Year Published: 2021
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!