Photo from wikipedia
The spatial resolution of a detector is a very important parameter for x-ray imaging. A bulk scintillation detector because of spreading of light inside the scintillator does't have a good… Click to show full abstract
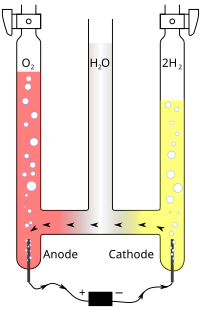
The spatial resolution of a detector is a very important parameter for x-ray imaging. A bulk scintillation detector because of spreading of light inside the scintillator does't have a good spatial resolution. The nanowire scintillators because of their wave guiding behavior can prevent the spreading of light and can improve the spatial resolution of traditional scintillation detectors. The zinc oxide (ZnO) scintillator nanowire, with its simple construction by electrochemical deposition in regular hexagonal structure of Aluminum oxide membrane has many advantages. The three dimensional absorption of X-ray energy in ZnO scintillator is simulated by a Monte Carlo transport code (MCNP). The transport, attenuation and scattering of the generated photons are simulated by a general-purpose scintillator light response simulation code (OPTICS). The results are compared with a previous publication which used a simulation code of the passage of particles through matter (Geant4). The results verify that this scintillator nanowire structure has a spatial resolution less than one micrometer.
Journal Title: Journal of Instrumentation
Year Published: 2018
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!