Photo from wikipedia
Odontogenesis is a complex physiological process that is based on dental tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs). Dental tissue-derived MSCs are the stem cell populations isolated and characterized from different parts… Click to show full abstract
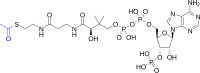
Odontogenesis is a complex physiological process that is based on dental tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs). Dental tissue-derived MSCs are the stem cell populations isolated and characterized from different parts of the oral cavity, and are considered as promising candidates for stem cell-based therapy. During odontogenesis, epigenetic factors can influence the proliferation, differentiation, or apoptosis of dental tissue-derived MSCs. As one of the epigenetic modifications, histone acetylation modification is critical for the proper regulation of many biological processes, including transcriptional regulation of cell cycle progression and cell fate. In odontogenesis, histone acetylation and deacetylation play crucial roles in odontogenic differentiation of dental tissue-derived MSCs. In this review, we aim to outline the general features of acetylation modification and describe their roles in odontogenic differentiation of dental tissue-derived MSCs, as well as their future implications in the field of novel regenerative therapies for the dentine-pulp complex.
Journal Title: Cellular reprogramming
Year Published: 2022
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!