Photo from wikipedia
In mitosis, while the importance of kinetochore (KT)-microtubule (MT) attachment has been known for many years, increasing evidence suggests that telomere dysfunctions also perturb chromosome segregation by contributing to the… Click to show full abstract
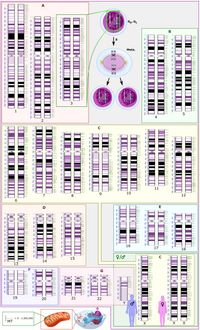
In mitosis, while the importance of kinetochore (KT)-microtubule (MT) attachment has been known for many years, increasing evidence suggests that telomere dysfunctions also perturb chromosome segregation by contributing to the formation of chromatin bridges at anaphase. Recent evidence suggests that Aurora B kinase ensures proper chromosome segregation during mitosis not only by controlling KT-MT attachment but also by regulating telomere and chromosome arm separation. However, whether and how Aurora B governs telomere separation during meiosis has remained unknown. Here, we show that fission yeast Aurora B localizes at telomeres during meiosis I and promotes telomere separation independently of the meiotic cohesin Rec8. In meiosis II, Aurora B controls KT-MT attachment but appears dispensable for telomere and chromosome arm separation. Likewise, condensin activity is nonessential in meiosis II for telomere and chromosome arm separation. Thus, in meiosis, the requirements for Aurora B are distinct at centromeres and telomeres, illustrating the critical differences in the control of chromosome segregation between mitosis and meiosis II.
Journal Title: Molecular Biology of the Cell
Year Published: 2020
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!