Photo from wikipedia
Motivation: Receptor mediated entry is the first step for viral infection. However, the question of how viruses select receptors remains unanswered. Results: Here, by manually curating a high‐quality database of… Click to show full abstract
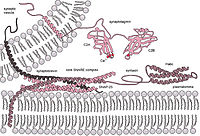
Motivation: Receptor mediated entry is the first step for viral infection. However, the question of how viruses select receptors remains unanswered. Results: Here, by manually curating a high‐quality database of 268 pairs of mammalian virus‐host receptor interaction, which included 128 unique viral species or sub‐species and 119 virus receptors, we found the viral receptors are structurally and functionally diverse, yet they had several common features when compared to other cell membrane proteins: more protein domains, higher level of N‐glycosylation, higher ratio of self‐interaction and more interaction partners, and higher expression in most tissues of the host. This study could deepen our understanding of virus‐receptor interaction. Availability and implementation: The database of mammalian virus‐host receptor interaction is available at http://www.computationalbiology.cn:5000/viralReceptor. Supplementary information: Supplementary data are available at Bioinformatics online.
Journal Title: Bioinformatics
Year Published: 2019
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!