Photo from wikipedia
MOTIVATION Predicting secondary structure and solvent accessibility of proteins are among the essential steps that preclude more elaborate 3D structure prediction tasks. Incorporating class label information contained in templates with… Click to show full abstract
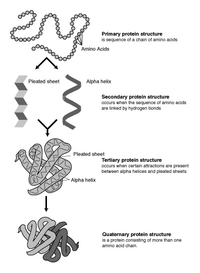
MOTIVATION Predicting secondary structure and solvent accessibility of proteins are among the essential steps that preclude more elaborate 3D structure prediction tasks. Incorporating class label information contained in templates with known structures has the potential to improve the accuracy of prediction methods. Building a structural profile matrix is one such technique that provides a distribution for class labels at each amino acid position of the target. RESULTS In this paper, a new structural profiling technique is proposed that is based on deriving PFAM families and is combined with an existing approach. Cross-validation experiments on two benchmark datasets and at various similarity intervals demonstrate that the proposed profiling strategy performs significantly better than Homolpro, a state-of-the-art method for incorporating template information, as assessed by statistical hypothesis tests. AVAILABILITY The DSPRED method can be accessed by visiting the PSP server at http://psp.agu.edu.tr. Source code and binaries are freely available at https://github.com/yusufzaferaydin/dspred. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary data are available at Bioinformatics online.
Journal Title: Bioinformatics
Year Published: 2019
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!