Photo from wikipedia
Meiosis is a specialized cell division that produces haploid gametes required for sexual reproduction. During the first meiotic division, homologous chromosomes pair and undergo reciprocal crossing over, which recombines linked… Click to show full abstract
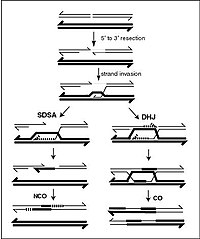
Meiosis is a specialized cell division that produces haploid gametes required for sexual reproduction. During the first meiotic division, homologous chromosomes pair and undergo reciprocal crossing over, which recombines linked sequence variation. Meiotic recombination frequency varies extensively both within and between species. In this review, we will examine the molecular basis of meiotic recombination rate variation, with an emphasis on plant genomes. We first consider cis modification caused by polymorphisms at the site of recombination, or elsewhere on the same chromosome. We review cis effects caused by mismatches within recombining joint molecules, the effect of structural hemizygosity, and the role of specific DNA sequence motifs. In contrast, trans modification of recombination is exerted by polymorphic loci encoding diffusible molecules, which are able to modulate recombination on the same and/or other chromosomes. We consider trans modifiers that act to change total recombination levels, hotspot locations, or interactions between homologous and homeologous chromosomes in polyploid species. Finally, we consider the significance of genetic variation that modifies meiotic recombination for adaptation and evolution of plant species.
Journal Title: Journal of experimental botany
Year Published: 2017
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!