Photo from wikipedia
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS REFERENCES • Omadacycline (OMC) is the first aminomethylcycline in late-stage clinical development – Aminomethylcyclines are semisynthetic antibiotics related to the tetracyclines that overcome the 2 main mechanisms of tetracycline… Click to show full abstract
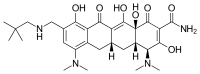
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS REFERENCES • Omadacycline (OMC) is the first aminomethylcycline in late-stage clinical development – Aminomethylcyclines are semisynthetic antibiotics related to the tetracyclines that overcome the 2 main mechanisms of tetracycline resistance, efflux pumps and ribosomal protection1-4 • OMC demonstrates potent, broad-spectrum in vitro activity against common Gram-positive aerobes (including methicillinand penicillin-resistant strains), Gram-negative aerobes, anaerobes, and atypical bacterial pathogens4,5 • Non-clinical and early clinical studies suggested that OMC had the potential to have a favorable cardiovascular profile – OMC had no effect on hERG channel activity or QTc, and demonstrated an overall low potential for cardiac arrhythmia or clinically significant cardiovascular toxicity. OMC inhibited binding of acetylcholine to the M2-subtype of the muscarinic receptor, resulting in a nonadrenergic, vagolytic effect6 – A phase 1, single-dose, randomized study demonstrated that OMC was associated with asymptomatic increases in heart rate but did not prolong the QT/QTc intervals in healthy adults7 • OMC has completed phase 3 clinical development as an intravenous (IV) to once-daily oral monotherapy for community-acquired bacterial pneumonia (CABP) and acute bacterial skin and skin structure infections (ABSSSI). OMC was generally safe and welltolerated – OMC was non-inferior to moxifloxacin (MOX) as an IV to once-daily oral antibiotic for CABP, and was active against the most common CABP pathogens including macrolide-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae (OPTIC)8 – OMC was also non-inferior to linezolid as an IV to once-daily oral antibiotic for ABSSSI, and was active against the most common ABSSSI pathogens including methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) (OASIS-1)9
Journal Title: Open Forum Infectious Diseases
Year Published: 2017
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!