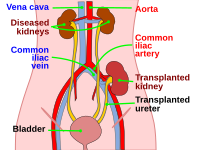
Photo from wikipedia
Abstract With the rapid aging of the global population posing a serious problem, frailty, a non-specific state that reflects physiological senescence rather than aging in time, has become more widely… Click to show full abstract
Abstract With the rapid aging of the global population posing a serious problem, frailty, a non-specific state that reflects physiological senescence rather than aging in time, has become more widely addressed by researchers in various medical fields. A high prevalence of frailty is found among kidney transplant (KT) candidates and recipients. Therefore, their frailty has become a research hotspot in the field of transplantation. However, current studies mainly focus on the cross-sectional survey of the incidence of frailty among KT candidates and recipients and the relationship between frailty and transplantation. Research on the pathogenesis and intervention is scattered, and relevant review literature is scarce. Exploring the pathogenesis of frailty in KT candidates and recipients and determining effective intervention measures may reduce waiting list mortality and improve the long-term quality of life of KT recipients. Therefore, this review explains the pathogenesis and intervention measures for frailty in KT candidates and recipients to provide a reference for the formulation of effective intervention strategies.
Journal Title: Chinese Medical Journal
Year Published: 2023
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!