Photo from wikipedia
BACKGROUND Prenatal myelomeningocele repair by open surgery can improve the neurological prognosis of children with this condition. A shift towards a fetoscopic approach seems to reduce maternal risks and improve… Click to show full abstract
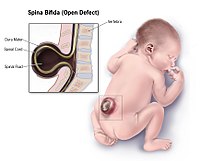
BACKGROUND Prenatal myelomeningocele repair by open surgery can improve the neurological prognosis of children with this condition. A shift towards a fetoscopic approach seems to reduce maternal risks and improve obstetric outcomes. OBJECTIVE The aim of this study was to report on the anaesthetic management of women undergoing prenatal open or fetoscopic surgery for neural tube defects. DESIGN A retrospective cohort study. SETTING Prenatal myelomeningocele repair research group, Vall d’Hebron University Hospital, Spain. INTERVENTION Intra-uterine foetal repairs of spina bifida between 2011 and 2016 were reviewed. Anaesthetic and vasoconstrictor drugs, fluid therapy, maternal haemodynamic changes during surgery, blood gas changes during CO2 insufflation for fetoscopic surgery, and maternal and foetal complications were noted. RESULTS Twenty-nine foetuses with a neural tube defect underwent surgery, seven (24.1%) with open and 22 (75.9%) with fetoscopic surgery. There were no significant differences in maternal doses of opioids or neuromuscular blocking agents. Open surgery was associated with higher dose of halogenated anaesthetic agents [maximum medium alveolar concentration (MAC) sevoflurane 1.90 vs. 1.50%, P = 0.01], higher need for intra-operative tocolytic drugs [five of seven (71.4%) and two of 22 (9.1%) required nitroglycerine, P = 0.001], higher volume of colloids (500 vs. 300 ml, P = 0.036) and more postoperative tocolytic drugs (three drugs in all seven cases (100%) of open and in one of 21 (4.76%) of fetoscopic surgery, P < 0.001). Median mean arterial pressure was lower in open than in fetoscopic surgery. SBP, DBP and mean blood pressure decreased during uterine exposure, and this descent was more acute in open surgery. Use of vasoconstrictor drugs was related to the time of uterine exposure, but not to surgical technique. Blood gas analysis was not affected by CO2 insufflation during fetoscopic surgery. CONCLUSION Open surgery was associated with more maternal haemodynamic changes and higher doses of halogenated anaesthetic and tocolytics agents than fetoscopic surgery.
Journal Title: European Journal of Anaesthesiology
Year Published: 2019
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!