Photo from wikipedia
Purpose of review This review summarizes the evidence describing functional mitral stenosis (MS) following surgical mitral valve repair. Recent findings Functional MS is an evolving concept and has been implicated… Click to show full abstract
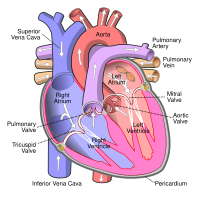
Purpose of review This review summarizes the evidence describing functional mitral stenosis (MS) following surgical mitral valve repair. Recent findings Functional MS is an evolving concept and has been implicated in the repair of functional and organic mitral regurgitation. Following repair of functional mitral regurgitation, an elevation in peak transmitral gradient and pulmonary artery pressure has been observed under physiologic stress. These changes have been associated with worse functional status early after restrictive annuloplasty. Following repair of organic mitral regurgitation, functional MS has also been observed and appears associated with worse functional status late after surgery. Summary Because repair of functional mitral regurgitation commonly involves restrictive annuloplasty, the issue of functional MS must be weighed against the benefits and durability of repair. Functional MS following repair of degenerative mitral regurgitation, however, may be modifiable. Research evaluating various repair techniques and their impact on functional MS following repair of organic is ongoing.
Journal Title: Current Opinion in Cardiology
Year Published: 2017
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!