Photo from wikipedia
OBJECTIVE To examine sharps injury (SI) rates among U.S. workers treated in hospital emergency departments. METHODS A national probability-based sample of approximately 67 U.S. hospital emergency departments from the National… Click to show full abstract
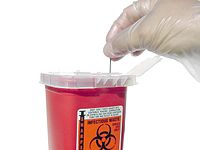
OBJECTIVE To examine sharps injury (SI) rates among U.S. workers treated in hospital emergency departments. METHODS A national probability-based sample of approximately 67 U.S. hospital emergency departments from the National Electronic Injury Surveillance System - Occupational Supplement was used to examine annual national estimates of SI rates (number of injuries/10,000 full-time equivalents) for U.S. workers from 2006-2020. RESULTS Among the general U.S. worker population, the 25-34-year age group experienced the highest annual SI rate. Healthcare industry workers experienced SI rates up to 16 times the rate of all U.S. workers. CONCLUSION Younger age (≤34 years) is associated with increased SI risk. Tailored prevention efforts should be developed to address the specific needs of these workers, especially among healthcare workers. Continual occupational surveillance will maximize the health and safety of U.S. workers.
Journal Title: Journal of occupational and environmental medicine
Year Published: 2023
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!