Photo from wikipedia
Rationale: Antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) combined with acute coronary syndrome (ACS) is rarely reported. Patient concerns: One male patient with APS was admitted to our hospital, who had recent unstable angina… Click to show full abstract
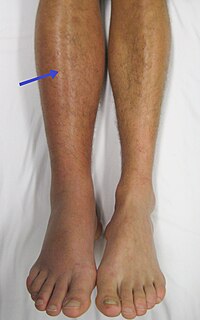
Rationale: Antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) combined with acute coronary syndrome (ACS) is rarely reported. Patient concerns: One male patient with APS was admitted to our hospital, who had recent unstable angina (UA). Diagnosis: The preliminary diagnosis of ACS and UA (BraunwaldiB) was then made. Interventions: This patient received secondary preventative therapy for coronary heart disease (CHD) in combination with percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty (PTCA) and implantation of NeoVas Bioresorbable Coronary Scaffold. Outcomes: The patient was followed up, without new UA episodes were observed at 6 months, 1 year, and 2 year after surgery, respectively. Lessons: It was thus concluded that percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) is effective for APS patients and NeoVas scaffold implantation is presumed safe.
Journal Title: Medicine
Year Published: 2018
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!