Photo from wikipedia
Abstract Rationale: Growing teratoma syndrome is defined as an increase in tumor size during or after systemic chemotherapy for germ cell tumors. These cases involve normal tumor maker levels and… Click to show full abstract
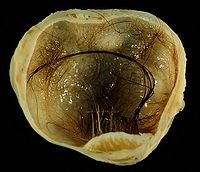
Abstract Rationale: Growing teratoma syndrome is defined as an increase in tumor size during or after systemic chemotherapy for germ cell tumors. These cases involve normal tumor maker levels and histological features of only mature teratoma. We report a rare case of an ovarian immature teratoma in a Japanese child that was diagnosed as growing teratoma syndrome. Patient concerns: A 12-year-old girl presented a painful abdominal mass. She underwent left salpingo-oophorectomy for grade 1 immature teratoma in the left ovary. She did not undergo additional chemotherapy or radiotherapy. Four months later, she presented with grade 3 immature teratoma disseminated into the abdomen and pelvis. Chemotherapy resulted in the tumor maker levels returning to their normal ranges, although the tumors had grown slightly. Diagnosis: The specimens resected by laparotomy after the chemotherapy consisted of mature tissue predominantly, although primitive neuroepithelium was observed in a small part of the specimen. The pathological diagnosis was grade 1 immature teratoma, notwithstanding the clinical diagnosis was growing teratoma syndrome based on the clinical features and pathogenesis. Interventions: Laparotomy was performed at 7 months after the first operation, with resection of various tumors as well as the rectum, sigmoid colon, residual left fallopian duct, and a small part of the ileum and omentum. Some small tumors at the parietal peritoneum were ablated, although many tiny tumors around the uterus were left untreated. Outcomes: The patient has been free from recurrence for 5 years. Lessons: Growing teratoma syndrome can develop in children, and their tumor size is comparable to that in adolescents and adults. Furthermore, development of growing teratoma syndrome from a primary germ cell tumor is presumably faster in children than in adolescents and adults. Complete resection of all growing teratoma tissue is recommended, although fertility-sparing surgery should be considered when possible.
Journal Title: Medicine
Year Published: 2020
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!