Photo from wikipedia
Purpose of review Patients with type 1 diabetes and end stage renal disease face a complex choice when considering the relative risks and benefits of kidney transplant alone with or… Click to show full abstract
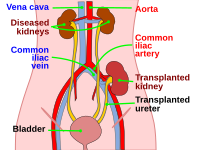
Purpose of review Patients with type 1 diabetes and end stage renal disease face a complex choice when considering the relative risks and benefits of kidney transplant alone with or without subsequent pancreas after kidney transplant (PAK) or simultaneous kidney pancreas transplant (SPK). Recent findings SPK is considered the optimal treatment regarding long-term patient survival, but when also faced with the option of living donor kidney transplant with the potential for PAK later, the ideal option is less clear. Summary This review summarizes the current literature regarding SPK, living donor kidney transplant alone, and PAK transplant outcomes and examines the relative risks of pre- and posttransplant variables that impact patient and graft survival to help inform this complex treatment decision.
Journal Title: Current Opinion in Organ Transplantation
Year Published: 2017
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!