Photo from wikipedia
Coronary computed tomography angiography (CCTA) is a validated technique for the evaluation of patients with suspected coronary artery disease, showing high accuracy compared with invasive coronary angiography and high negative… Click to show full abstract
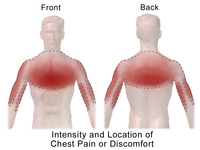
Coronary computed tomography angiography (CCTA) is a validated technique for the evaluation of patients with suspected coronary artery disease, showing high accuracy compared with invasive coronary angiography and high negative predictive value. CCTA is also well positioned as a first-line test for the evaluation of stable chest pain. This purpose of this review is to examine the evidence behind CCTA in the setting of stable chest pain, with attention to 5 key strengths of a CCTA-based approach: (1) effective gatekeeping to cardiac catheterization, (2) selective discrimination for revascularization and tailored medical therapy, (3) advanced risk stratification, (4) improvement in outcomes, and (5) support from multisociety guidelines. Given the expansion of CT technologies to include functional strategies for evaluating ischemia both with and without vasodilators, CCTA is poised to become the comprehensive examination for stable chest pain and anginal equivalent cardiopulmonary symptoms.
Journal Title: Journal of Thoracic Imaging
Year Published: 2019
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!