Photo from wikipedia
Do anti-Xa levels effect VTE in trauma patients? Should we be targeting levels with our chemoprophylaxis? This sytematic review evaluates these questions with some surprising outcomes. BACKGROUND Trauma patients have… Click to show full abstract
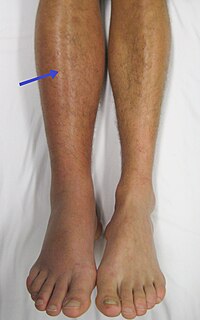
Do anti-Xa levels effect VTE in trauma patients? Should we be targeting levels with our chemoprophylaxis? This sytematic review evaluates these questions with some surprising outcomes. BACKGROUND Trauma patients have simultaneously high venous thromboembolism (VTE) and bleeding risk. Optimal chemoprophylaxis regimens remain unclear. This study aims to answer three questions for trauma patients. Is there any association between anti-Xa and VTE? Does dose adjustment improve prophylactic anti-Xa rates? Does dose adjustment improve anti-Xa adequacy and VTE compared with standard dosing? METHODS Systematic search of MEDLINE, Embase, Scopus, and Web of Science occurred in May 2021. Two author reviews included trauma studies that evaluated low molecular weight heparin chemoprophylaxis, reported anti-Xa level, and evaluated more than one outcome. Data were dually extracted and estimated effects were calculated using RevMan 5.4 applying the Mantel-Haenszel method. Analysis 1 compared patients with peak anti-Xa of 0.2 IU/mL or greater or trough 0.1 IU/mL or greater to those with lower anti-Xa using VTE as the primary outcome. Analysis 2 reported the effect of dose adjustment on anti-Xa. Analysis 3 compared standard dosing to dose adjustment with the primary outcome being anti-Xa adequacy; secondary outcomes were VTE, pulmonary embolism, and bleeding complications. RESULTS There were 3,401 studies evaluated with 24 being included (19 retrospective studies, 5 prospective studies). In analysis 1, achieving adequate anti-Xa was associated with reduced odds of VTE (4.0% to 3.1%; odds ratio [OR], 0.52; p = 0.03). Analysis 2 demonstrated that 768 (75.3%) patients achieved prophylactic anti-Xa with adjustment protocols. Analysis 3 suggested that dose-adjusted chemoprophylaxis achieves prophylactic anti-Xa more frequently (OR, 4.05; p = 0.007) but without VTE (OR, 0.72; p = 0.15) or pulmonary embolism (OR, 0.48; p = 0.10) differences. In subgroup analysis, anti-Xa dose adjustment also suggested no VTE reduction (OR, 0.68; p = 0.08). CONCLUSION Patients with higher anti-Xa levels are less likely to experience VTE, and anti-Xa guided chemoprophylaxis increases anti-Xa adequacy. However, dose adjustment, including anti-Xa guided dosing, may not reduce VTE. LEVEL OF EVIDENCE Systematic Review Meta-Analysis, Level IV.
Journal Title: Journal of Trauma and Acute Care Surgery
Year Published: 2022
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!