Photo from wikipedia
Importance: Early detection of pneumothorax, most often on chest radiograph (CXR), can help determine need for emergent clinical intervention. The ability to accurately detect and rapidly triage pneumothorax with an… Click to show full abstract
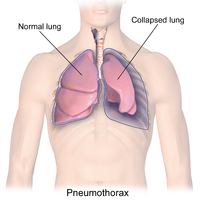
Importance: Early detection of pneumothorax, most often on chest radiograph (CXR), can help determine need for emergent clinical intervention. The ability to accurately detect and rapidly triage pneumothorax with an artificial intelligence (AI) model could assist with earlier identification and improve care. Objective: This study aimed to compare the accuracy of an AI model (Annalise Enterprise) to consensus thoracic radiologist interpretations in detecting (1) pneumothorax (incorporating both non-tension and tension pneumothorax) and (2) tension pneumothorax. Design: A retrospective standalone performance assessment was conducted on a dataset of 1,000 CXR cases. Setting: The cases were obtained from four hospitals in the United States. Participants: The cases were obtained from patients aged 18 years or older. They were selected using two strategies from all CXRs performed at the hospitals including inpatients and outpatients. The first strategy identified consecutive pneumothorax cases through a manual review of radiology reports and the second strategy identified consecutive tension pneumothorax cases using natural language processing. For both strategies, negative cases were selected by taking the next negative case acquired from the same x-ray machine. The final dataset was an amalgamation of these processes. Methods: Each case was interpreted independently by up to three radiologists to establish consensus ground truth interpretations. Each case was then interpreted by the AI model for the presence of pneumothorax and tension pneumothorax. Main Outcome: The primary endpoints were the areas under the receiver operating characteristic curves (AUCs) for the detection of pneumothorax and tension pneumothorax. The secondary endpoints were the sensitivities and specificities for the detection of pneumothorax and tension pneumothorax at predefined operating points. Results: Model inference was successfully performed in 307 non-tension pneumothorax, 128 tension pneumothorax and 550 negative cases. The AI model detected pneumothorax with AUC of 0.979 (94.3% sensitivity, 92.0% specificity) and tension pneumothorax with AUC of 0.987 (94.5% sensitivity, 95.3% specificity). Conclusions and Relevance: The assessed AI model accurately detected pneumothorax and tension pneumothorax on this CXR dataset. Its use in the clinical workflow could lead to earlier identification and improved care for patients with pneumothorax.
Journal Title: JAMA Network Open
Year Published: 2022
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!