Photo from wikipedia
The transition between shear-flowing and shear-arrested states of frictional granular matter is studied using constant-stress discrete element simulations. By subjecting a dilute system of frictional grains to a constant external… Click to show full abstract
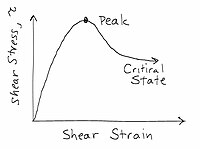
The transition between shear-flowing and shear-arrested states of frictional granular matter is studied using constant-stress discrete element simulations. By subjecting a dilute system of frictional grains to a constant external shear stress and pressure, friction-dependent critical shear stress and density are clearly identified with both exhibiting a crossover between low and high friction. The critical shear stress bifurcates two nonequilibrium steady states: (i) steady state shear flow characterized by a constant deformation rate, and (ii) shear arrest characterized by temporally decaying creep to a statically stable state. The onset of arrest below critical shear stress occurs at a time t_{c} that exhibits a heavy-tailed distribution, whose mean and variance diverge as a power law at the critical shear stress with a friction-dependent exponent that also exhibits a crossover between low and high friction. These observations indicate that granular arrest near critical shear stress is highly unpredictable and is strongly influenced by interparticle friction.
Journal Title: Physical review letters
Year Published: 2019
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!