Photo from wikipedia
Botnets are widespread nowadays with the expansion of the Internet and commonly occur in many cyber-attacks, resulting in serious threats to network services and users’ properties. With the rapid development… Click to show full abstract
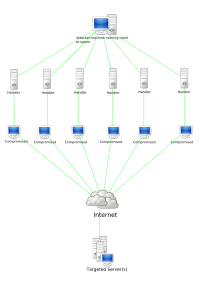
Botnets are widespread nowadays with the expansion of the Internet and commonly occur in many cyber-attacks, resulting in serious threats to network services and users’ properties. With the rapid development of the Internet of Things (IoT) applications, the botnet can easily make use of IoT devices for larger-scale attacks. Domain name system (DNS) is widely used by the botnet to establish the connection between bots and their corresponding command-and-control (C&C). In order to avoid the track of the C&C through the DNS information, some sophisticated schemes are used by the botnet and fast-flux is a typical one. In this paper, the activities of Rustock botnet domain names which just use the fast-flux as the connection method between bots and C&C, are deeply analyzed from multiple aspects. Besides, we extract 32 special features of Rustock domain named querying traffic. Then multiple popular classifiers are adopted in order to pick the malicious domain names out from the DNS traffic using those 32 features. The work of this paper aims to provide guidance for future botnet detection based on real statics and experiments.
Journal Title: IEEE Access
Year Published: 2019
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!