Photo from wikipedia
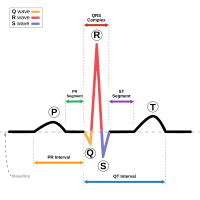
We developed a novel method for QRS complex and P wave detection in the electrocardiogram (ECG) signal. The approach reconstructs two different signals for the purpose of QRS and P… Click to show full abstract
We developed a novel method for QRS complex and P wave detection in the electrocardiogram (ECG) signal. The approach reconstructs two different signals for the purpose of QRS and P wave detection from the modes obtained by the complete ensemble empirical mode decomposition with adaptive noise, taking only those modes that best represent the signal dynamics. This approach eliminates the need for conventional filtering. We first detect QRS complex locations, followed by removal of QRS complexes from the reconstructed signal to enable P wave detection. We introduce a novel method of P wave detection from both the positive and negative amplitudes of the ECG signal and an adaptive P wave search approach to find the true P wave. Our detection method automatically identifies P waves without prior information. The proposed method was validated on two well-known annotated databases—the MIT BIH Arrythmia database (MITDB) and The QT database (QTDB). The QRS detection algorithm resulted in 99.96% sensitivity, 99.9% positive predictive value, and an error of 0.13% on all validation databases. The P wave detection method had better performance when compared to other well-known methods. The performance of our P wave detection on the QTDB showed a sensitivity of 99.96%, a positive predictive value of 99.47%, and the mean error in P peak detection was less than or equal to one sample (4 ms) on average.
Journal Title: IEEE Access
Year Published: 2019
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!