Photo from wikipedia
To improve the accuracy of soil heavy metal content prediction, this study proposes a dynamic neural network optimization model (DNNOM). The model is based on a radial basis function neural… Click to show full abstract
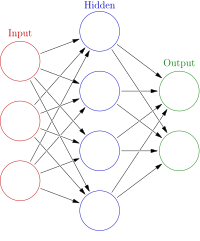
To improve the accuracy of soil heavy metal content prediction, this study proposes a dynamic neural network optimization model (DNNOM). The model is based on a radial basis function neural network (RBFNN). The weights and bias of the output layer of the RBFNN were generated using an adaptive dynamic genetic optimization algorithm (ADGOA), and the center point of the hidden layer of the RBFNN was determined using an efficient density peak clustering algorithm (EDPC). An adaptive variance measure (AVM) was then used to generate the width vector of RBFNN hidden layer. The model was applied to the predict soil heavy metal content in six new urban areas in Wuhan. Through comparison with support vector machine(SVM), light gradient boosting machine(LightGBM), RBFNN, and genetic algorithm optimizes the radial basis function neural network(GA-RBFNN), the experimental results demonstrate that the DNNOM is closer to the real value than the other four models, and the four error indicator values are also significantly lower than those of the other comparison models, which have higher prediction accuracy. Especially when compared with RBFNN, the MAPE and SMAPE of DNNOM decreased by 3.98% and 3.9%, respectively.
Journal Title: IEEE Access
Year Published: 2022
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!