Photo from wikipedia
We develop new methods of quantifying the impact of photon detector imperfections on possible secret key rates in Time-Entanglement based Quantum Key Distribution (QKD). We address photon detection timing jitter,… Click to show full abstract
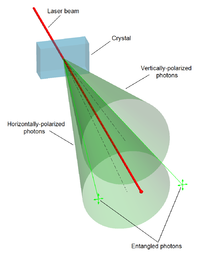
We develop new methods of quantifying the impact of photon detector imperfections on possible secret key rates in Time-Entanglement based Quantum Key Distribution (QKD). We address photon detection timing jitter, detector downtime, and dark photon counts and show how each may decrease the maximum achievable secret key rate differently. We begin with a standard Discrete Memoryless Channel (DMC) model to get a good bound on the mutual information lost due to the timing jitter, then introduce a novel Markov Chain (MC) based model to characterize the effect of detector downtime and show how it introduces memory to the key generation process. Finally, we propose a new method of including dark counts in the analysis that shows how dark counts can be especially detrimental when using the common Pulse Position Modulation (PPM) for key generation. Our results show that these three imperfections can significantly reduce the achievable secret key rate when using PPM for QKD. One of our main results is providing tooling for experimentalists to predict their systems’ achievable secret key rate given the detector specifications.
Journal Title: IEEE Transactions on Communications
Year Published: 2022
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!