Photo from wikipedia
Fuzzy cognitive maps (FCMs) play an important role in high-level reasoning but are limited in their ability to model complex systems with singularities. We are interested in systems that exhibit… Click to show full abstract
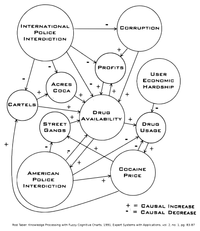
Fuzzy cognitive maps (FCMs) play an important role in high-level reasoning but are limited in their ability to model complex systems with singularities. We are interested in systems that exhibit discontinuous behaviors as one or more of their internal node states approach a threshold. In a new approach to FCM dynamics, we define general classes of aggregation functions which “jump” to a boundary value when any input crosses a threshold, or when all inputs do. The threshold value is a context-dependent parameter which can be readily understood by subject matter experts. Aggregation functions are applied separately to positively and negatively causal antecedents to each node then combined to form the nodal state. This modeling is applied in Computing with Words (CWW) settings, in which link strengths and activation levels are elicited using vocabulary words represented by interval type-2 fuzzy membership functions. We illustrate the behaviors of these novel FCM systems in comparison with their nonsingularity versions.
Journal Title: IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems
Year Published: 2020
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!