Photo from wikipedia
The use of high‐throughput DNA sequencing (HTS) has revolutionized the assessment of biodiversity in plant and animal communities. There are two main approaches to estimate the identity and the relative… Click to show full abstract
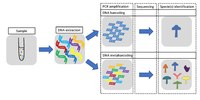
The use of high‐throughput DNA sequencing (HTS) has revolutionized the assessment of biodiversity in plant and animal communities. There are two main approaches to estimate the identity and the relative species abundance (RSA) in complex mixtures using HTS: amplicon metabarcoding and shotgun metagenomics. While amplicon metabarcoding targets one or a few genomic regions, shotgun metagenomics randomly explores the genome of the species. In this issue of Molecular Ecology Resources, Wagemaker et al. (2021) present a new method, multi‐species Genotyping by Sequencing (msGBS), as an alternative middle ground between metabarcoding and metagenomics. They apply the technique to mixtures of plant roots and report the remarkable capacity of msGBS to estimate the RSA. If validated in other laboratories and biological communities, msGBS might become a third method to explore the biodiversity of biological communities, especially of plants, where current techniques are struggling to get sufficient taxonomic resolution.
Journal Title: Molecular Ecology Resources
Year Published: 2021
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!