Photo from wikipedia
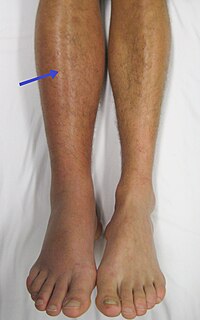
Currently Direct Oral Anticoagulants (DOACs) are licensed for treatment of deepvein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE) whereas warfarin is licensed for all venous thrombosis (VTE). Warfarin, with lowmolecularweight heparin… Click to show full abstract
Currently Direct Oral Anticoagulants (DOACs) are licensed for treatment of deepvein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE) whereas warfarin is licensed for all venous thrombosis (VTE). Warfarin, with lowmolecularweight heparin (LMWH) during the acute initial phase, is therefore the standard agent for longterm anticoagulation for patients with thrombosis at other sites. The large phase 3, randomised, controlled trials comparing the DOACs: dabigatran, rivaroxaban, apixaban and edoxaban with warfarin in DVT and PE patients, did not include those with thrombosis at unusual sites.
Journal Title: British Journal of Haematology
Year Published: 2022
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!